Research Highlight
Machine Learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer science, machine learning (ML) deals with the study and use of data and algorithms that mimic how humans learn. This helps machines gradually improve their accuracy. ML allows software applications to improve their prediction accuracy without being specifically programmed to do so. It estimates new output values by using historical data as input.
There are three main types of machine learning:
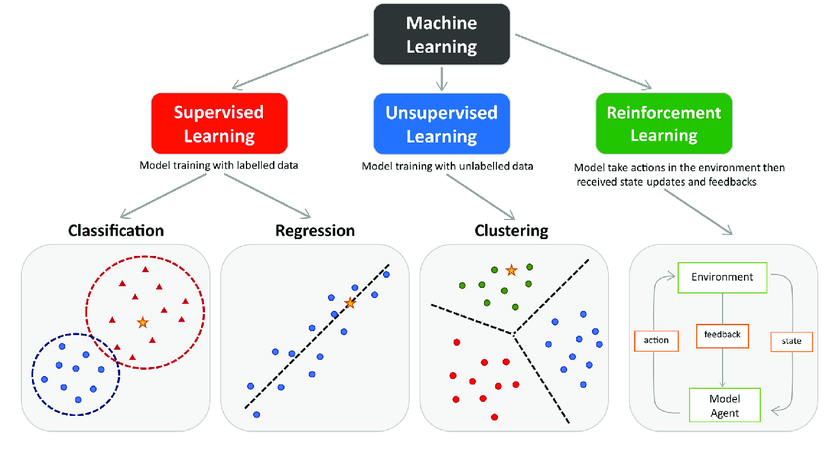
- Supervised Learning: In this type, the model is trained on a dataset consisting of pairs of input data and expected output. The goal is to learn a mapping from input data to expected output, so that it can later predict outputs for new data.
- Unsupervised Learning: In this type, the model is trained on unlabeled data. The goal is to discover underlying structures in the data, such as clusters or transformations, without knowing the expected output beforehand.
- Reinforcement Learning: This type is particularly suited for decision-making and control. The model interacts with a dynamic environment and learns from reinforcement feedback (rewards or penalties) based on the actions it takes. The system’s objective is to find an optimal strategy to maximize rewards.
Machine learning is widely applied in various fields, from information technology, healthcare, finance, to manufacturing and services. Specific applications include image and speech recognition, financial market prediction, medical diagnosis, autonomous driving, and many more. This is leading to significant improvements in performance and automation capabilities across various domains.
